 | 
The Malaysian Educational Policy
The Ministry of Education is responsible in drawing up the National Education Policy based on the National Ideology or commonly referred to as the "Rukunegara" adhering to Malaysia's aspiration of unity and development.
Principles of Rukunegara
Belief in God
Loyalty to King and Country
Upholding the Constitution
Rule of Law
Good Behaviour and Morality
Underlying objectives of Rukunegara
To develop a united nation within a plural society
To develop a democratic society through a constitutionally elected Parliament
To develop a just society with equal opportunities for all
To develop a liberal society of diverse cultural traditions
To develop a progressive society oriented towards science and modern technology
Aims of Government Educational Programme and activities
In Malaysia, they are designed to among others:-
1. Equip students with the essential skills in a holistic and integrated manner, in order to produce individuals who are intellectually, spiritually, emotionally and physically balanced; as well as functionally literate;
2. Incalcate and nurture national consciousness by promoting common ideals, values, aspirations and loyalties to foster national unity and national identity;
3. Produce skilled manpower for economic and national development;
4. Instill desired moral values in students so that they can contribute effectively towards nation building
Revamping of the National Curriculum
Since the last ten years the curriculum has been revamped to meet the needs of the country. Among them are the adoption of the "Kurikulum Bersepadu Sekolah Rendah" - "KBSR", "3R's" (Reading, Writing and Arithmatic), "Kurikulum Bersepadu Sekolah Menengah" ,"KBSM" creation of "Smart Schools" and "Visionary Schools".
Stressing the important aspects of citizenship, national unity and moral development, living skills (manipulative skills, entrepreneurship and family life education), languages (communicative skills) and information technology.
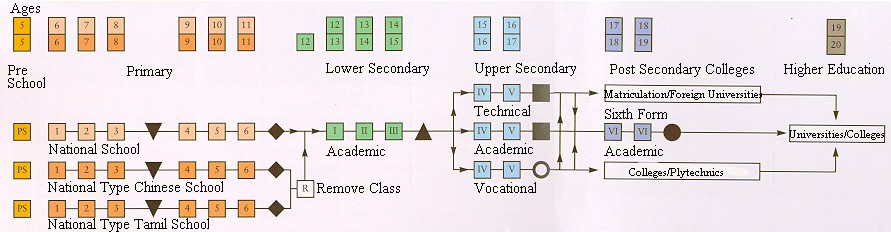
Public Education System in Malaysia
Please refer to the above chart on the general public education system adopted. As far as possible the government has provided free primary education for all the citizen in the country.
Types of Curriculum available
In Malaysia there are several types of primary and secondary schools. They are divided based on their vernacular languages. All follows the national curriculum and use the Malay language - "Bahasa Malaysia" as the medium of instruction along with their vernacular languages as a subject.
The Chinese or Tamil schools students prior to the promotion to Form 1, they have to undergo a year in "Remove Form" to enable them to adapt to the national curriculum effectively.
Types of establishment available:
A. Primary Schools;
1. National Primary School
2. National Type Chinese School
3. National Type Tamil School
4. National Type Arabic School
B. Secondary Schools;
5. National Secondary School
6. National Type Arabic School
7. Secondary Technical School
8. National Residential School
C. Teacher Training Colleges
D. College Education
E. Polytechnic Education
F. Universities
The six years of primary education provides good foundation for the students prior entry into secondary level. The existence of continuous assessments is for monitoring the development of the student and to identify the problems in the teaching-learning process. At the end of the six years, the student will sit for the "Primary School Assessment Test" - "PSAT" or "Ujian Pendidikan Sekolah Rendah" - "UPSR".
After completing the first three years at secondary school level, students will sits for their "Lower Secondary Assessment" - "LSA" or "Penilaian Menengah Rendah" - "PMR" which corresponds to the Lower Certificate of Education Examination.
After completing year five (four and five), students will take their "Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia" - "SPM" or also known as "Malaysian Certificate of Education" - "MCE" which corresponds to GCE "O" level. These examinations are divided into several streams such as arts, science, technical and vocational.
After year five, there are two types of pre-university education offered. The most common ones are the Form Six. After completing year six and seven, students will sits for their "Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia" - "STPM" or "Higher School Certificate" - "HSC" which corresponds to the GCE "A" level.
But for residential schools students are offered alternative to the "STPM". They normally undergo matriculation course designed and monitored by selected public universities.
Meanwhile for the courses at the levels of Teachers Training College, Colleges, Polytechnics and universities, the undergraduates or graduates undergo similar programmes like their counterparts worldwide.
Beside the above, there are also a number of educational facility offered by other ministries such as the Ministry of Youths and Sports and Ministry of Public Enterprises. Examples are community colleges, skills institutes, youths educational centres and cooperative institute.
Private Education
In Malaysia, the establishment of private educational centres or schools is governed mainly by three legal documents. They are the Education Act, 1961, The Essential (Higher Education Institution) Regulation, 1969 and the Universities and University Colleges Act, 1971.
Private education in Malaysia consists of the following categories:-
1. Pre-School Education
2. Private Primary and Secondary Education
a. Regular private educational institutions
b. Chinese private educational institutions
c. Expatriate private educational institutions/International schools
3. Skills Training Institutes
4. Tuition Centres
5. Language Centres
6. Private Educational Colleges (for post secondary level)
7. Private Universities
|
 |
 |
SCHOOLING TERMS IN 2001
GROUP A
Schools in Kedah, Kelantan and Terengganu
Start/End Schooling
02-01-2001 18-01-2001
29-01-2001 24-05-2001
05-06-2001 06-09-2001
19-09-2001 08-11-2001
GROUP B
Schools in Perlis,Penang,Perak,
Selangor,Kuala Lumpur,Labuan,
Negeri Sembilan,Malacca,Johor,
Pahang,Sabah and Sarawak
Start/End Schooling
03-01-2001 19-01-2001
29-01-2001 25-05-2001
06-06-2001 06-09-2001
19-09-2001 08-11-2001
Total No. of Schooling inclusive of Public Holidays..........202 days
Total No. of School Holidays.......91 days
SCHOOL HOLIDAYS
For Kedah,Kelantan and Terengganu
From/To
19.01.2001 28.01.2001
25.05.2001 04.06.2001
07.09.2001 18.09.2001
09.11.2001 05.01.2002
While for Perlis,Penang,Perak,Selangor,Kuala Lumpur,Negeri Sembilan,Malacca,Johor,Pahang,Labuan,Sabah and Sarawak
From/To
20.01.2001 28.01.2001
26.05.2001 05.06.2001
07.09.2001 18.09.2001
09.11.2001 06.01.2002
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|  |
 |
 |
HIGHLIGHTS EXAMINATION IN 2001
Examination/Date
Penilaian Tahap Satu (PTS)
withdrawn
Ujian Pencapaian Sekolah Rendah (UPSR)
3 September - 5 September
Penilaian Menengah Rendah (PMR)
16 October - 19 October
Sijil Tinggi Agama Malaysia (STAM)
Oral 16 July 27 July
Written 22 - 31 October
Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (July)
Malay Language 30 Jun
Matematics 23 Jun
Selection Examination for promotion to Form Six & Matriculation (UPTEM)
11 November
Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM)
Oral Malay Language 02 July 13 July
Oral English Language 6 Aug-17 Aug
Planning 01 October - 02 October
Practical 03 October 11 Oktober
Information Technology 16 October - 31 October
Written 05 November - 28 November
Sijil Tinggi Pelajaran Malaysia (STPM)
05 November - 28 November
|
Welcome/Appreciation Our organization welcomes the Honourable Patron,Chairman, learned and knowledgeable panel of Advisers and took this opportunity to record our appreciation for their kind consent and continuous support.
|
|



